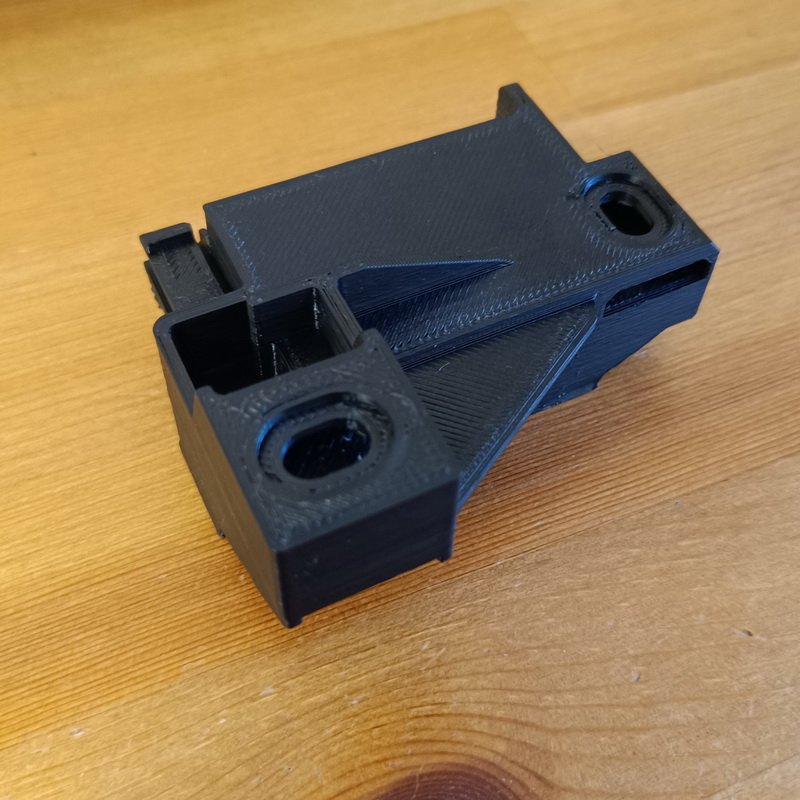
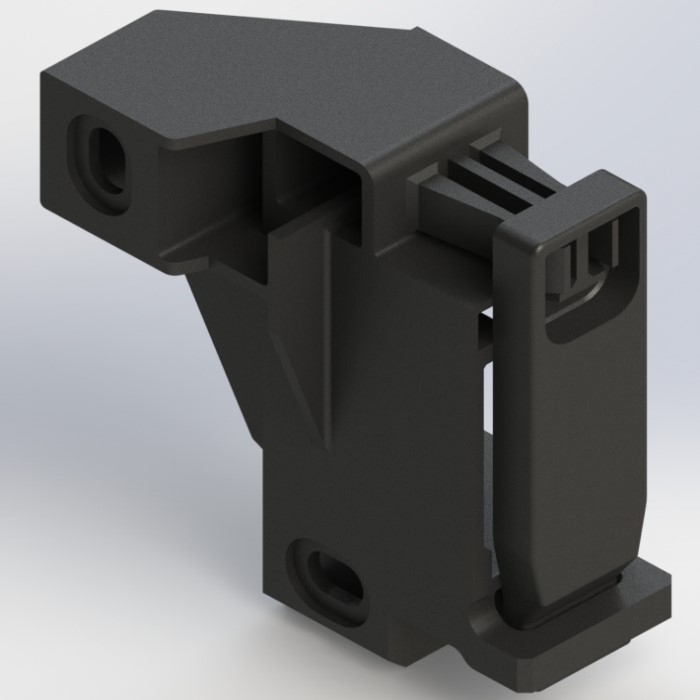
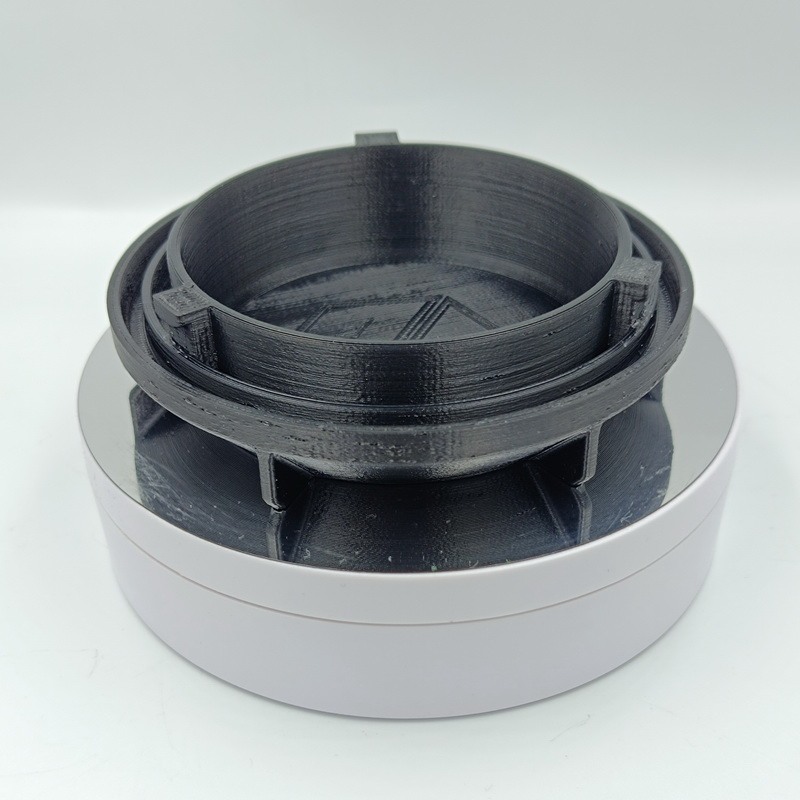
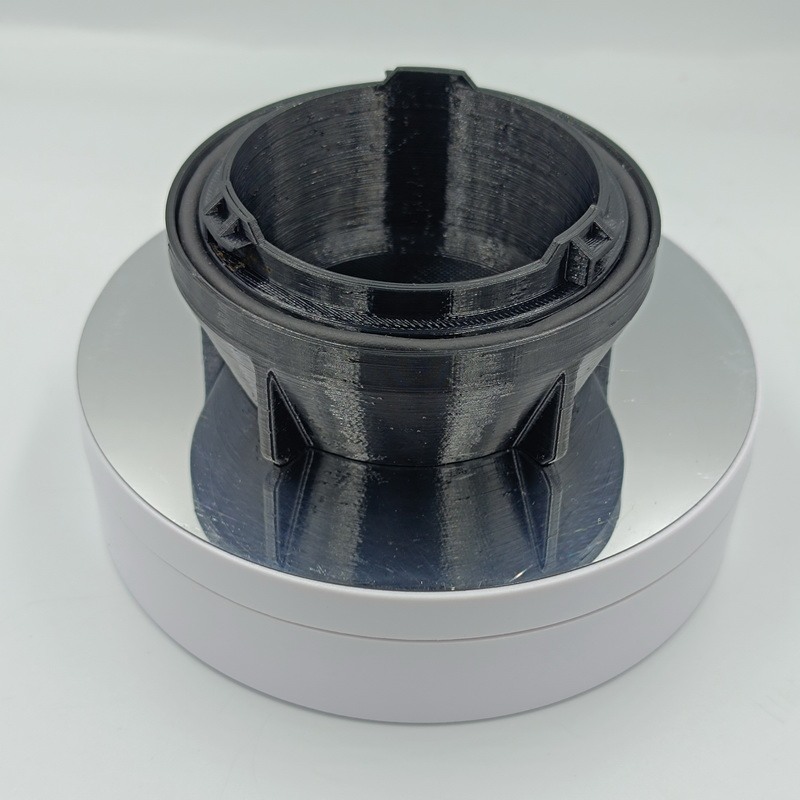
Fused Deposition Modeling – FDM Printing – Technology Overview
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) is a widely adopted 3D printing technology that utilizes thermoplastic filaments with diameters of 1.75 mm and 3.0 mm to create parts. The FDM 3D printing process encompasses the following steps:
1. Printing Process
FDM operates by melting and extruding thermoplastic filaments through a heated nozzle. The nozzle moves along the X and Y axes, depositing molten material layer by layer to build the part. The build platform moves along the Z axis, enabling the creation of intricate geometries.
2. Material Selection
FDM can print with a broad range of thermoplastic filaments, including ABS, PLA, PETG, nylon, TPU, and more. Material choice depends on specific applications and mechanical requirements.
3. Surface Finish
Surface finish on FDM parts is generally coarser compared to other 3D printing technologies like SLA or SLS. Post-processing methods such as sanding, polishing, or painting can enhance surface quality.
4. Accuracy
FDM parts are typically less accurate compared to other 3D printing technologies due to limitations in the extrusion process. Layer height and nozzle diameter impact the achievable level of detail, and parts may exhibit visible layer lines.
5. Size
FDM printers are available in a wide range of sizes, from compact desktop machines to large industrial systems. Build volume depends on the specific printer, but most FDM printers can produce parts ranging from 200 x 250 x 250 mm to 500 x 500 x 500 mm.
6. Cost
FDM stands out as one of the most cost-effective 3D printing technologies, making it accessible across various sectors, from home users to small and medium businesses. The cost of FDM printers and materials has significantly decreased since its introduction, offering numerous affordable options.
7. Strength
FDM parts are typically strong and durable, with mechanical properties influenced by the chosen material and print parameters. Layer adhesion and infill density can affect the part’s strength and rigidity.
In conclusion, Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) is a versatile and economical 3D printing technology widely used for prototyping, tooling, and small-batch production. FDM can print with a diverse range of materials, and the resulting parts are generally robust and long-lasting. However, FDM parts may exhibit a rough surface finish, and their accuracy is limited compared to other 3D printing technologies (up to 0.5 mm depending on part size). When selecting a 3D printing technology, it’s important to consider project-specific requirements and choose the technology that best aligns with your needs.